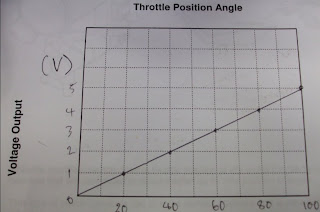
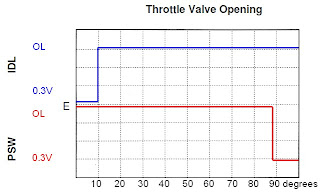
My oxygen sensor has 4 wires, and is a zirconia type switching sensor.
The max voltage is around 0.9V and the min is about 0.1V.
At idle this sensor read 10 cross counts in 10 seconds.
 This picture is from 1997 Encyclopedia Britannia, Inc
This picture is from 1997 Encyclopedia Britannia, Inc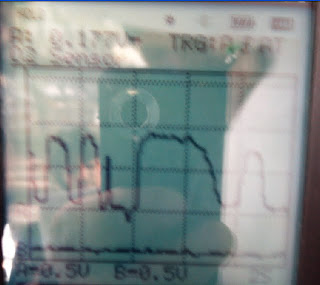 This shows sudden deceleration this shows the mixture going lean, and giving a low voltage of 0.15V
This shows sudden deceleration this shows the mixture going lean, and giving a low voltage of 0.15V
This shows sudden acceleration as the mixture turns rich, and gives a high voltage. Reaches 0.9V at max.
 This shows the response time of the O2 sensor. It takes roughly 100ms to fully change the fuel/air mix via the O2 sensor to ECU.
This shows the response time of the O2 sensor. It takes roughly 100ms to fully change the fuel/air mix via the O2 sensor to ECU.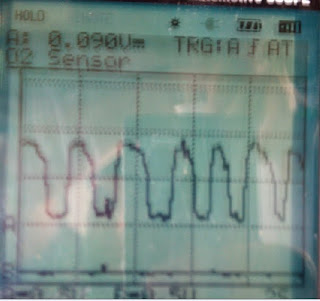 This is at 2500RPM, as it is cruising the ECU is oscillating the fuel/air ratio to keep emissions down. As its at 2500 it oscillates quicker than at idle.
This is at 2500RPM, as it is cruising the ECU is oscillating the fuel/air ratio to keep emissions down. As its at 2500 it oscillates quicker than at idle.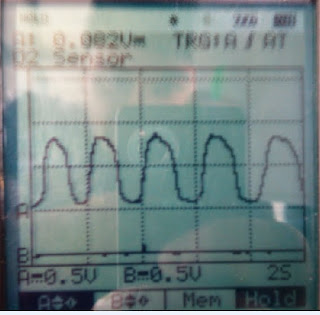 At idle this shows us that the air/fuel mix is changing to try and burn rich and lean, so that it produces the least amount of emssions.
At idle this shows us that the air/fuel mix is changing to try and burn rich and lean, so that it produces the least amount of emssions.I've found that my O2 sensor is a critcal part of the car, and thankfully it is working properly. Without this sensor, the car would fail emission tests and fuel economy tests.
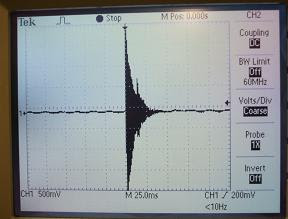




 V.
V.